3D printing has revolutionized the world of manufacturing and prototype development. At ELOPRINT, we take pride in utilizing a wide range of advanced 3D printing processes to deliver high-quality test adapters and electronic solutions to our customers. In this blog post, we would like to introduce you to our various 3D printing processes that enable us to create unique products.

Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Efficiency through Melted Material
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), is one of the most commonly used 3D printing processes. In FDM, melted plastic is extruded through a heated nozzle and applied layer by layer to create the desired object. What sets FDM apart is its impressive material versatility. Unlike some other methods, FDM is not limited to a specific material, allowing for the use of various thermoplastics and materials as needed, providing versatile design options. Additionally, FDM 3D printers and the required raw materials are comparatively affordable and easy to handle.
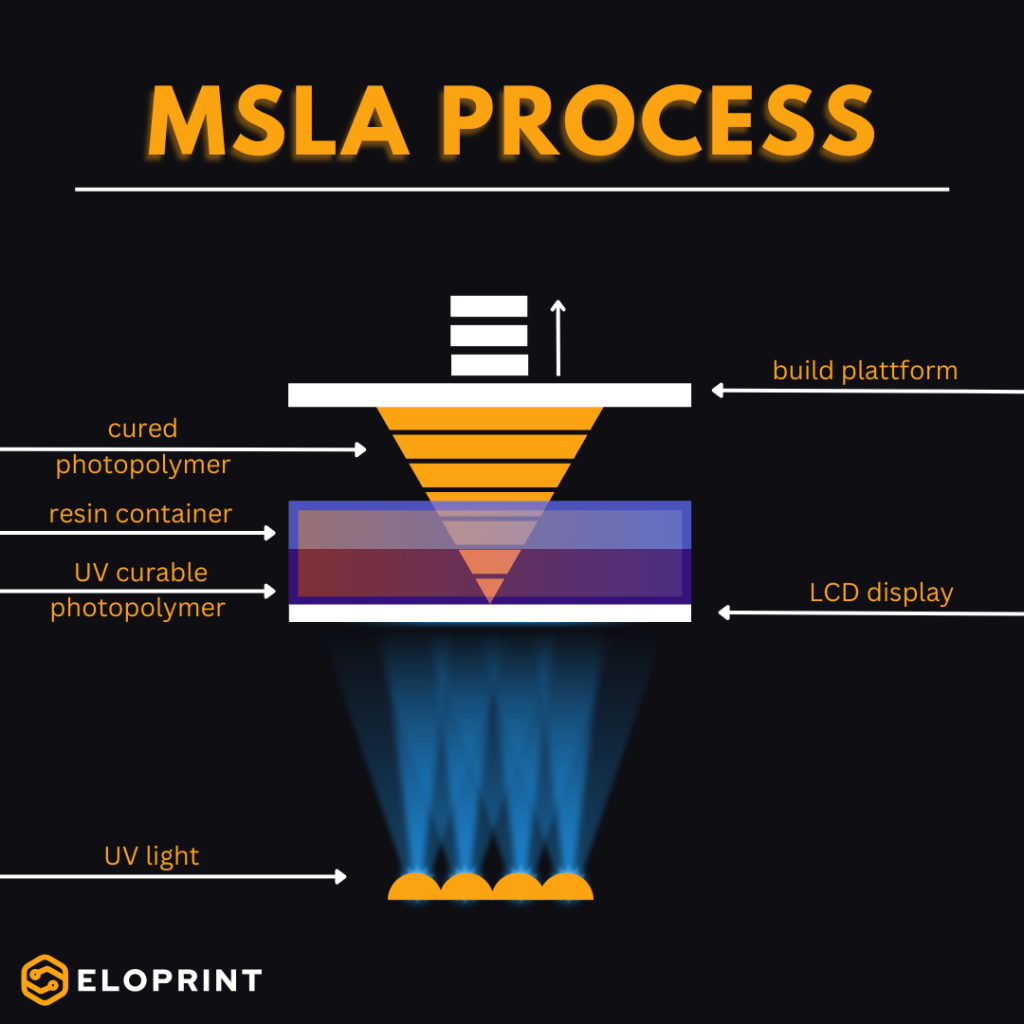
Masked Stereolithography (MSLA): Precision and Speed with Photopolymers
Masked Stereolithography (MSLA) is an advanced 3D printing technology based on the principles of stereolithography. In MSLA, a ultraviolet (UV) light source is used to selectively cure a liquid photopolymer resin layer by layer to create a 3D object. This process is controlled by a mask that determines where the UV light is directed to solidify the resin. What distinguishes MSLA is its exceptional detail accuracy and the ability to cure entire layers at once, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and small-batch production.
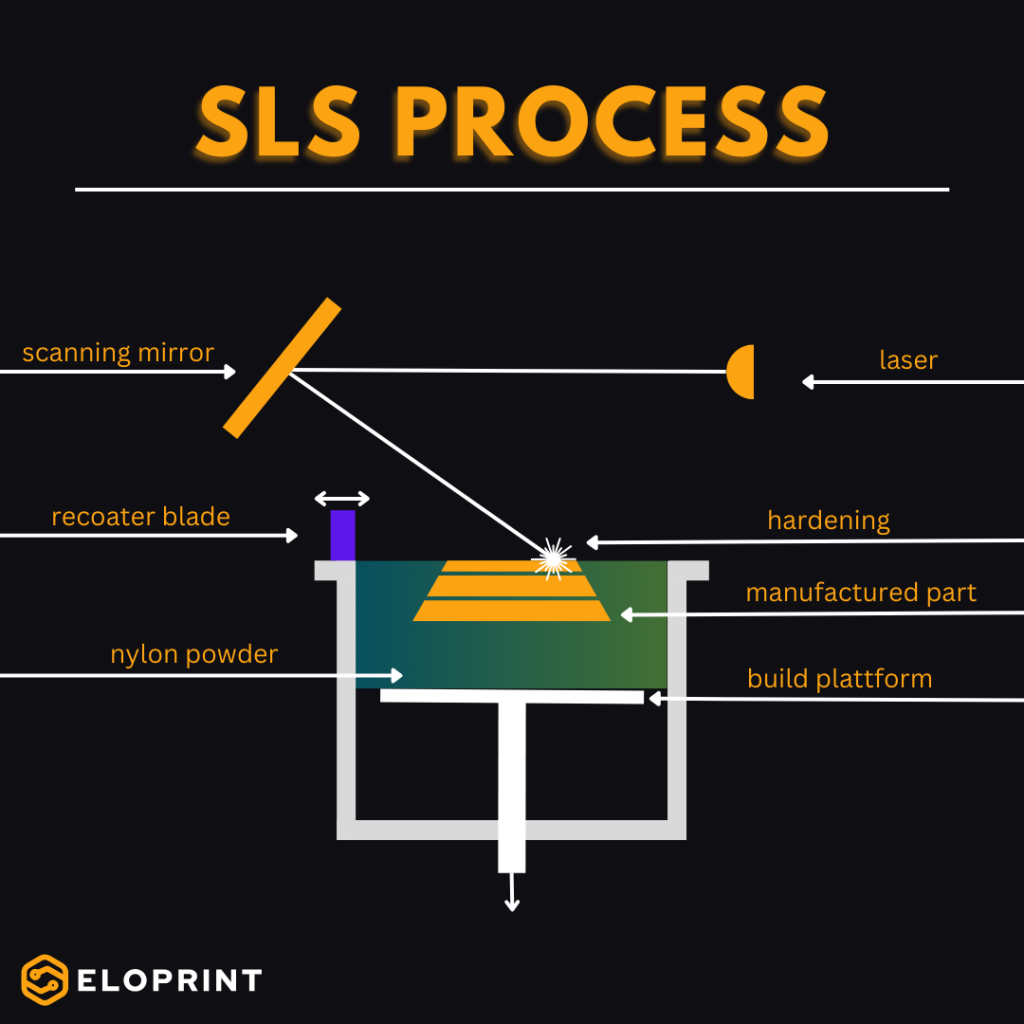
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Robust Precision
Masked Stereolithography (MSLA) is an advanced 3D printing technology based on the principles of stereolithography. In MSLA, a ultraviolet (UV) light source is used to selectively cure a liquid photopolymer resin layer by layer to create a 3D object. This process is controlled by a mask that determines where the UV light is directed to solidify the resin. What distinguishes MSLA is its exceptional detail accuracy and the ability to cure entire layers at once, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and small-batch production.
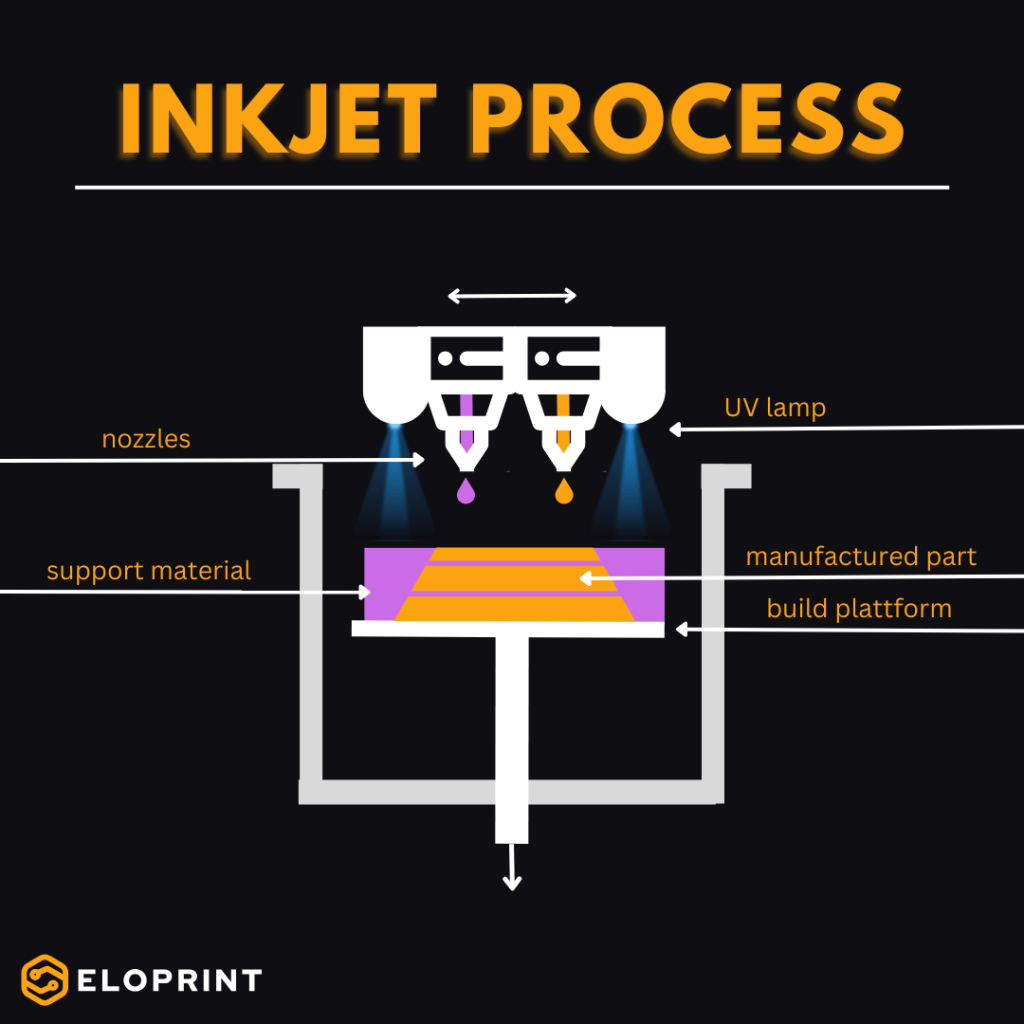
Inkjet: Precision for Complex Designs
In Inkjet 3D printing, a liquid photopolymer, similar to an inkjet printer, is applied to a print bed in the form of microscopic droplets. This plastic cures through a chemical reaction upon exposure to UV light. The inkjet printer operates with a UV lamp that cures the printed droplets after each layer is printed. The key advantage lies in the ability to print a water-soluble support material in addition to the build material. This allows for the inclusion of complex and overhanging geometries in support material, enabling the creation of nearly any geometry with the highest precision. Thus, Inkjet technology provides the flexibility to manufacture test adapters according to our customers‘ specific requirements and deliver high-quality solutions.
At ELOPRINT, we understand that every project is unique. Therefore, we carefully choose the most suitable 3D printing process to meet our customers‘ needs. With our variety of technologies, we can offer test adapters and electronic solutions that meet the highest quality standards while representing innovation and adaptability.
Contact us today to learn more about our 3D printing solutions and how we can meet your requirements.